"Delegative Leadership: Everything You Need To Know" explores a distinctive leadership approach based on the values of trust, independence, and autonomy.
This blog will arm you with the knowledge you need to successfully navigate the world of delegative leadership style, whether you're a leader looking to broaden your toolkit, a team member curious about how this approach might affect your workplace, or just someone curious about the dynamics of leadership styles.
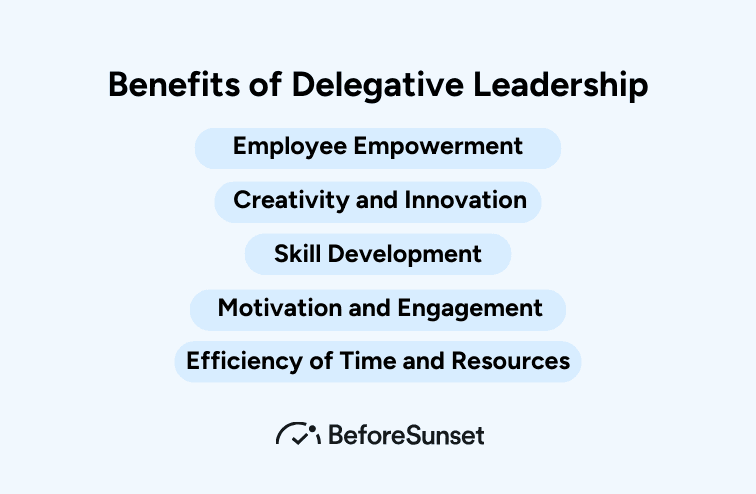
Benefits of Delegative Leadership
In the correct situations, delegation leadership skills may provide a number of advantages:
Employee Empowerment: By offering team members autonomy and decision-making authority, delegation fosters employee empowerment by fostering a sense of pride in and ownership over one's job.
Creativity and Innovation: Innovation and creativity in the workplace are fostered by encouraging team members to use their imaginations and come up with original solutions to issues.
Skill Development: Delegative leaders provide team members the chance to hone their leadership, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities, which may be beneficial for their future personal and professional success.
Motivation and Engagement: Employees are more likely to be motivated and engaged, which increases job satisfaction and productivity when they feel trusted and in charge of their work.
Efficiency of Time and Resources: Delegative approach to leadership frees the leader from micromanaging every part of their team's work, enhancing overall efficiency. This frees the leader to concentrate on higher-level activities and strategic planning.
Adaptability: Delegative leaders can be more adaptive in contexts that are changing quickly because they depend on the knowledge of their team to make quick judgments and adjust to changing circumstances.
Better Problem Solving: When team members are allowed the flexibility to make judgments, a varied range of viewpoints and problem-solving techniques can develop, which can result in more practical solutions.
Leadership Development: Delegative leadership approach may spot potential leaders within a group and provide them with chances to hone their abilities.
Laissez-Faire Leadership
Laissez-faire leadership, often known as the "hands-off" or "free-rein" style of leadership, is a distinctive and fascinating way to manage groups of people and organizations. Lending people a high degree of autonomy and self-governance is a priority in laissez-faire leadership, as opposed to more authoritarian or prescriptive leadership styles.
Definition of Laissez-Faire Leadership
Laissez-faire leadership, a term derived from the French expression "let them do," is characterized by a hands-off approach in which leaders provide little guidance and intervention, giving their team members or subordinates a significant amount of autonomy and freedom to make decisions and manage their tasks.
With this leadership approach, managers put their faith in their staff to be autonomous, accountable for their job, and confident in their capacity to make wise decisions and find solutions on their own.
A leader who practices laissez-faire leadership plays a more passive role, abstaining from micromanaging and being personally involved in day-to-day activities. Instead, they give their staff the freedom to take charge of their tasks, set their own procedures, and resolve problems.
This management style places a strong emphasis on individual initiative and accountability, and it encourages team members to use their creativity and critical thinking to achieve goals.
The idea that individuals closest to the tasks and issues are frequently best qualified to make informed judgments and develop the most practical solutions is one of the fundamental tenets of laissez-faire leadership. This leadership approach may develop independence and innovation by giving team members a high degree of autonomy.
To ensure that the team stays aligned with company goals and objectives, it is essential to keep lines of communication open, provide assistance and resources as needed, and strike a balance between flexibility and direction.
In circumstances when team members are knowledgeable, capable, and driven on their own, laissez-faire leadership may be quite effective. It enables them to flourish in a setting that respects their knowledge and gives them the freedom to take the lead.
However, it might not be appropriate in situations where team members need to be closely supervised, don't have the essential abilities, or if quick and decisive decision-making is required. In order to successfully apply the laissez-faire leadership style, a leader must be able to strike the correct balance between autonomy and engagement, tailoring their strategy to the unique requirements of their team as well as the circumstances at hand.
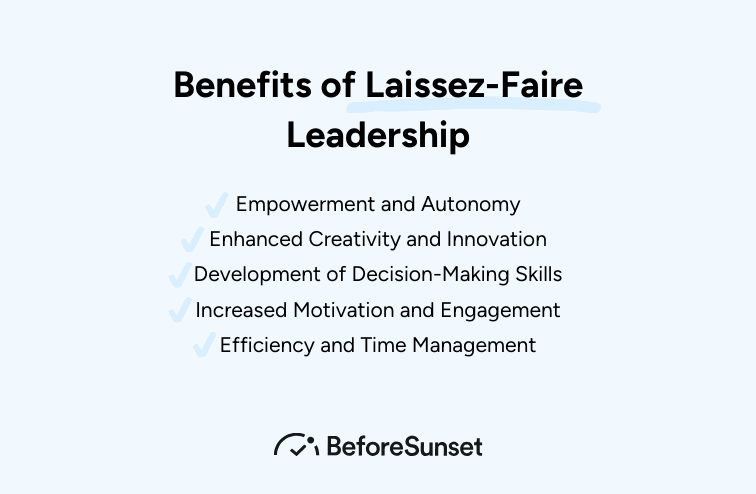
Benefits of Laissez-Faire Leadership
When used properly and under suitable conditions, laissez-faire leadership may provide the following advantages:
Empowerment and Autonomy: Team members are given a lot of autonomy, which may boost their confidence, make them feel like they have ownership of their jobs, and give them a sense of empowerment.
Enhanced Creativity and Innovation: Laissez-faire leadership promotes team members' independent problem-solving and innovative thinking. This may lead to creativity and a variety of thoughts.
Development of Decision-Making Skills: Team members have the chance to improve their ability to make decisions and solve problems, which may be beneficial for both their personal and professional development.
Increased Motivation and Engagement: Employees are more likely to be motivated and engaged, which increases job satisfaction and productivity when they feel trusted and accountable for their work. Motivated employees are important to become successful leaders.
Efficiency and Time Management: Laissez-faire leadership frees the leader from the need to micromanage day-to-day operations, which can result in enhanced efficiency. The leader can instead concentrate on strategic planning and higher-level duties.
Adaptability: This leadership approach can be more flexible in conditions that change quickly since team members are given the freedom to act quickly and adjust to changing circumstances.
Diverse Problem-Solving Approaches: Teams with autonomy are more likely to include team members who can contribute a variety of viewpoints and problem-solving techniques, which can result in more efficient solutions.
Leadership Development: Laissez-faire leadership may spot potential team captains and provide them with chances to hone their leadership abilities.
Challenges of Laissez-Faire Leadership
Laissez-faire leadership poses a number of difficulties due to its detached style. One of the main problems is the possibility of unclear direction and guidance, which can cause team members to feel uncertain and confused.
Particularly when people lack the required knowledge or competence, it might result in less-than-ideal decision-making. As it becomes difficult to place blame for actions or mistakes, accountability issues may arise. When team members request assistance but only receive modest support, they may become frustrated and have lower work satisfaction.
With beginner or inexperienced teams, this leadership style may not work well, and in certain cases, it may cause duties to be disregarded. In order for laissez-faire leadership to be successful, leaders must manage these difficulties by offering the proper ratio of autonomy to assistance based on the skills of their team and the unique circumstances.
Employee Satisfaction and Daily Tasks
Employee contentment is intimately related to the nature of routine duties. Job satisfaction often rises when employees regard their regular work to be interesting, relevant, and compatible with their abilities and goals.
Job satisfaction may be increased by tasks that give diversity, a challenge, and an opportunity to use one's skills, as well as by autonomy and decision-making power in one's everyday duties. Job happiness may also be greatly increased by giving employees consistent feedback, recognition, and a feeling of purpose through duties that are in line with their beliefs and professional aspirations.
The ability of teams to work well together, maintain a healthy work-life balance, and be influenced by company culture and leadership on everyday tasks are all critical factors in determining employee happiness.
Impact on Employee Satisfaction
Daily duties and employee happiness are linked in a cyclical connection that has a significant influence on one another. Employee happiness is substantially influenced by the type of everyday duties, and this in turn can have an impact on how employees approach and interact with their daily obligations. The way they interact is as follows:
1. Daily Tasks Impact on Employee Satisfaction:
Tasks that offer diversity and difficulty keep workers motivated and engaged, which increases job satisfaction.
When workers can use their knowledge and abilities in their work on a regular basis, they feel more appreciated and fulfilled.
Providing employees a sense of control and ownership over their work, and allowing them autonomy in everyday activities can improve job satisfaction.
Praising workers' efforts and accomplishments, regular feedback, and acknowledgment for well-done activities add to job satisfaction.
A sense of purpose and fulfillment is fostered by tasks that are in line with personal beliefs and professional ambitions.
Tasks that don't cause excessive stress or overwork as well as moderate workloads help to improve both job satisfaction and work-life balance.
2. Impact of Employee Satisfaction on Daily Tasks:
Contented workers are more driven and invested in their jobs, which has a favorable effect on the standard and effectiveness of everyday activities.
Job happiness can encourage creativity and originality in routine activities, which can enhance problem-solving and performance.
Happy workers frequently approach their daily activities with a more upbeat and proactive attitude, which may lead to greater productivity.
Employee interactions with coworkers are influenced by job satisfaction, which in turn impacts how cooperatively people do daily duties.
Happy workers are more inclined to offer helpful criticism and communicate clearly, which strengthens collaboration in the execution of everyday activities.
Daily Tasks and Responsibilities Under Delegative Management
Daily duties and tasks under delegative management constitute a unique style of teamwork and leadership. Team members are given a high level of autonomy in their everyday work under this leadership approach. They are free to choose the best strategies, come to conclusions, and find solutions without excessive intervention from the leader. This empowerment promotes a sense of accountability and independence by encouraging team members to take ownership of their duties and obligations.
In a delegative management setting, task distribution frequently requires teamwork. Team members may have the chance to take part in task allocation decisions, giving them the ability to select assignments that match their abilities and interests. This shared workload distribution may result in a more motivated and engaged staff.
Another essential component of everyday duties under delegated management is problem-solving. Team members are urged to come up with their own answers to problems they run against. This leadership strategy encourages team members to use their imagination and critical thinking, which may result in creative solutions and a wide variety of problem-solving techniques.
One of the main tenets of delegative management is accountability. Each team member is held accountable for their decisions and the results of their work. Due to the team members' awareness of the immediate consequences of their actions, this accountability fosters a strong feeling of ownership and dedication to the duties they are given.
Team members may also be responsible for time management, budgeting, and other aspects of resource allocation. They have the freedom to decide how best to maximize their output and the success of their everyday duties thanks to this degree of control.
Compared to more directive leadership styles, task monitoring is often less extensive under delegative management. Team members are trusted to manage their own work, with the team leader only offering direction and assistance when absolutely necessary. Maintaining the team's alignment with company goals and addressing potential challenges both depend on open and effective communication.
Delegative management can also encourage team members to enhance their skills. People who have more responsibility for their everyday responsibilities have the chance to improve their leadership, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities, which can be beneficial for their personal and professional growth.
Lack of Direction and Accountability for Employees
Employees who lack clear direction and accountability may suffer negative impacts on both a personal and corporate level. Employees may lose sight of their tasks and responsibilities in the absence of clear direction, which may cause confusion and dissatisfaction.
As a result, there may be inefficiencies, lower production, and disengagement among the employees. In addition, a lack of responsibility for outcomes and results might emerge from unclear accountability, making it difficult to pinpoint the culprits in the event of mistakes or problems.
Overall, a lack of responsibility and direction hurts not just an employee's performance but also the advancement and success of the company by compromising its ability to meet objectives and keep a motivated, cohesive staff.
Decision-Making Process for Employees Under Delegative Management
Employee decision-making is defined by a high level of autonomy and independence under delegative management. Team members are given the power to decide on matters pertaining to their work. Usually, this procedure consists of the following steps: Employees start by identifying any problems or difficulties they have with their regular work.
They then examine these problems while thinking about alternative tactics and solutions. Choosing the best course of action during the decision-making process requires taking into account the goals and broad direction established by the leader or organization.
Employees deploy the selected solution after making a choice and track its development. To get advice, communicate progress, and guarantee alignment with company goals, open communication with the leader and other team members is encouraged throughout this process.
This strategy fosters innovation and problem-solving abilities while also empowering staff to make well-informed decisions, which results in a more motivated and independent workforce.
Hands-Off Approach to Delegative Leadership
Laissez-faire leadership, often known as the "Hands-Off Approach to Delegative Leadership," is a management approach that places a high focus on autonomy and self-governance within a team or organization.
In this leadership paradigm, leaders give their team members a lot of latitude in making choices, handling day-to-day duties, and taking responsibility for their work. While playing a supporting and consultative role, the team's leader avoids micromanaging and lets team members choose their own strategies and solutions.
As team members are given the freedom to solve problems on their own, this strategy promotes independence, creativity, and individual accountability.
Advantages of a Hands-Off Approach to Delegative Leadership
Laissez-faire leadership, often known as a "Hands-Off Approach to Delegative Leadership," has a number of benefits. Giving team members a high degree of autonomy and decision-making authority empowers them, which can increase their sense of self-worth and ownership over their jobs.
As team members experiment with new ideas and methodologies, this autonomy, coupled with little interference, fosters creativity and innovation. Additionally, it gives kids a chance to hone their problem-solving and decision-making abilities.
Employees who feel trusted and accountable are frequently more engaged and driven, which increases work satisfaction and productivity. Additionally, the leader may concentrate on strategic duties, increasing productivity. This method enables the team to adjust quickly in circumstances that change quickly, making it a useful leadership style when used with experienced and motivated people in situations where creative thinking is essential.
Disadvantages of a Hands-Off Approach to Delegative Leadership
While a hands-off approach to delegative leadership has certain benefits, it also has some serious drawbacks. The main disadvantage is the potential for unclear oversight and guidance, which can cause team members' bewilderment and uneasiness.
Team members may find it difficult to make well-informed judgments, efficiently prioritize activities, or resolve challenging problems in the absence of clear direction. Additionally, this absence of oversight may lead to problems with accountability, making it challenging to place blame for mistakes or unsuccessful results.
Additionally, some team members could grow irritated when they need direction or support but only get a little help, which might lower morale and decrease work satisfaction. This type of leadership works best when used sparingly and with self-motivated, experienced people, but it may not be appropriate when more intensive monitoring and coaching are required for optimum performance and productivity.
Transformational Leadership Versus Delegation Leadership
Delegative leadership and transformational leadership are two separate leadership philosophies, each with a unique set of traits and benefits.
Leaders who inspire and drive their team members to produce extraordinary results are considered to possess transformational leadership. These leaders are often visionaries who provide a compelling future vision, establish high standards, and motivate their teams to go beyond their own boundaries.
By putting a strong emphasis on personal growth and development, they foster an environment that is both intellectually stimulating and empowering. Transformational leaders frequently set an example for their team and inspire others to do the same. High levels of participation and dedication, as well as innovation, are all fostered exceptionally well by this strategy.
Contrarily, delegation is a more hands-off style of leadership in which team members are given a great deal of autonomy and decision-making power by the leader. In this approach, team members are trusted to make choices, address issues, and handle their jobs with little oversight. While playing a supporting role, the leader avoids micromanaging.
Delegative leadership may not be successful in settings demanding tight supervision or rapid, authoritative decision-making, but it may be successful when team members are knowledgeable and self-motivated.
The Role of Leadership Styles in Enhancing Employee Engagement
In the ever-evolving business landscape, understanding and implementing various leadership styles is crucial for boosting employee engagement and morale. Among the myriad of leadership approaches, democratic leadership, delegative leadership, and servant leadership stand out for their unique benefits and contributions to the workplace.
Democratic Leadership: Promoting Participation and Innovation
Democratic leadership is a style where leaders actively involve team members in the decision-making process. This approach fosters a culture of trust, where communication skills are vital. By valuing input from individual employees, democratic leaders create an environment where innovative solutions can thrive. This inclusive approach not only enhances employee motivation but also aligns with the common goal of achieving organizational objectives.
Delegative Leadership: Empowering Teams with Autonomy
In a delegative leadership approach, leaders grant team members the freedom to make their own decisions with minimal oversight. This style is effective in creative industries and situations requiring independent decisions and quick decision-making. Delegative leaders focus on task delegation, allowing employees to take ownership of their tasks. This not only improves employee morale but also fosters a high level of trust within the team. Here are the benefits and challenges of delegative leadership:
Benefits:
Employee Autonomy: Empowering employees to make autonomous decisions enhances their sense of ownership and accountability.
Continuous Improvement: Encourages employees to engage in continuous improvement and innovative problem-solving.
Challenges:
Lack of Direction: Without clear guidance, employees might feel lost and unproductive.
Accountability Issues: Determining responsibility can be challenging in a highly autonomous environment.
Servant Leadership: Prioritizing Team Members’ Needs
Servant leadership revolves around the principle of prioritizing the needs of the team over the leader’s own interests. Servant leaders focus on the continuous improvement of their team members, promoting a supportive environment where emotional intelligence is key. This style is particularly effective in enhancing employee engagement and fostering a strong sense of community and mutual respect.
Effective Leadership Strategies for Organizational Success
Combining elements from various common leadership styles can lead to highly effective leadership strategies. For instance, integrating the participatory nature of democratic leadership with the autonomy of delegative leadership and the supportive focus of servant leadership can create a balanced approach that meets diverse team needs. This blend can drive continuous improvement, align with organizational goals, and create a culture of trust.
Key Strategies:
Task Delegation: Use a balanced approach to delegation, ensuring employees are well-supported while maintaining autonomy.
Emotional Intelligence: Leaders should develop strong emotional intelligence to understand and address the needs of their team effectively.
Conclusion
Adopting and adapting different leadership styles to suit specific team dynamics and organizational goals can significantly enhance employee engagement, morale, and overall productivity. By understanding the strengths and challenges of each approach, leaders can create a supportive, innovative, and high-performing work environment.
Delegative Leadership: The Role of BeforeSunset AI for Teams
In the realm of delegative leadership, where autonomy and innovation are paramount, leveraging advanced tools like BeforeSunset AI can significantly enhance team productivity and employee engagement.
By integrating AI-powered solutions into the delegative leadership approach, leaders can maintain the delicate balance between granting independence and ensuring accountability.
AI-Powered Workspace: Promoting Teamwork and Reducing Burnout
BeforeSunset AI's asynchronized team workspace is designed to promote teamwork while respecting individual privacy and preventing burnout.
This aligns perfectly with the delegative leadership approach, where leaders empower team members to make independent decisions and manage their tasks with minimal oversight.
By reducing distractions and providing comprehensive analytics, BeforeSunset AI helps create an environment where team members can focus on their common goals and enhance their leadership skills.
Key Features for Delegative Leaders:
Set Goals with Team Tags: Leaders can categorize to-dos and set specific goals with team tags, ensuring clarity and focus.
Analyze and Track Progress: The platform offers tools to track and analyze the team's achievements and workload, making it easier for leaders to provide the right amount of support and direction.
Check Employee Well-Being: By gathering team time stats, moods, and statuses, leaders can monitor the well-being of their team members and take proactive steps to prevent burnout, thus fostering a supportive and motivating environment.
Manage Capacity and Resources: Leaders can get an overview of each member's progress, allowing for better resource management and ensuring that team members are not overburdened.
Work-Life Balance and Effective Communication:
BeforeSunset AI also facilitates a healthy work-life balance by allowing team members to separate and control their work and personal to-dos on a single platform.
This is crucial in a delegative leadership setting, where employee autonomy is valued, and effective leadership strategies involve respecting personal boundaries.
Fostering Team Bonding and Emotional Intelligence:
Understanding the importance of emotional intelligence in servant leadership, BeforeSunset AI enables leaders to know their teammates' moods and personal interests, thereby enhancing team bonding and creating a culture of trust.
This helps servant leaders prioritize their team members' needs and promote a sense of community within the organization.
Conclusion:
Integrating BeforeSunset AI into a delegative leadership framework can significantly enhance team performance, employee engagement, and overall job satisfaction.
By providing the tools needed to balance autonomy with support, leaders can foster an environment where innovation thrives, and organizational goals are met with minimal oversight and maximum efficiency.


